The popularity of monolithic buildings is growing, while the use of reinforced concrete blocks and bricks in construction is increasingly being abandoned.
The reason lies in the advantages of monolithic structures: they allow you to increase the number of storeys, provide ample opportunities for space planning and at the same time require lower construction costs. The result is high quality buildings at low cost. One of the most important advantages of monolithic structures is that their walls are stronger than brick and reinforced concrete and can withstand heavy loads. However, this advantage is preserved only if the walls were made with high quality. Their reliability and strength largely depend on what formwork was used in construction.
Formwork is a structure with the help of which a concrete solution is given the desired shape. In fact, this is the frame of the future building, which is filled with concrete mixture and left until it hardens. Typically, wall formwork consists of the following elements:
- Support frame.
- Formwork panel.
- Fasteners including screws, wedges and universal locks.
- Stiffening rib.
Types of formwork
There are three types of construction:
- Removable, which is dismantled after the solution has completely dried. This formwork is assembled from separate parts. The result is a collapsible structure that can be dismantled and reused. Among the advantages of this type of formwork are ease of installation and the possibility of reuse, which significantly reduces the financial costs of construction.
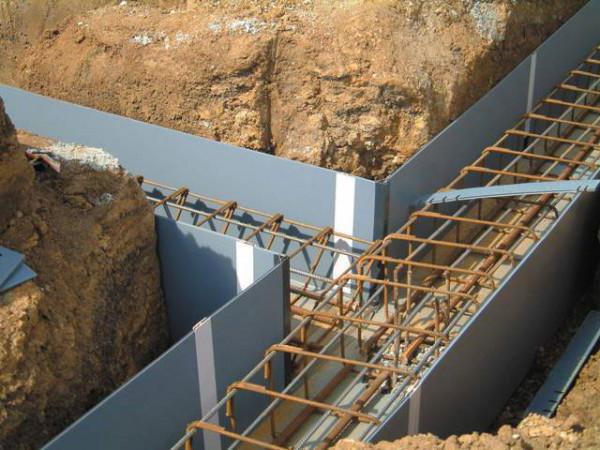

- Fixed, respectively, one that cannot be dismantled. Installation of formwork of this type is carried out mainly from expanded polystyrene or polystyrene foam. It remains part of the structure being built. And at the same time it acts as insulation.
- “Floating” formwork is typical for the construction of a monolithic foundation, which is immersed in the ground. It is a shield assembled from boards, which is slightly higher in height than the planned concrete structure. The shield is lowered into the pit and attached to its walls. Cardboard or roofing felt is rolled out on top of it.
There are also several types depending on the purpose:
- Wall formwork. Its installation is carried out for the construction of vertical structures and walls.
- Horizontal, which is used for installing foundations and floors.
- Curved, which allows you to fill parts of unusual shapes.
Installation and dismantling of each type of formwork has its own characteristics. You need to know them to perform quality work.
What is formwork
Formwork is an auxiliary structure. It serves as the basis for creating foundations for residential and industrial buildings, fences, garages and other structures. Formworks have been used in construction since ancient times. The development of technology for their installation is inextricably linked with the development of architecture, and these structures should not be treated with disdain.
Formwork is a box-shaped structure, a frame into which concrete is poured. The shields of the structure do not allow the solution to spread until it “sets.” After the hardening process is completed, the formwork is usually dismantled.
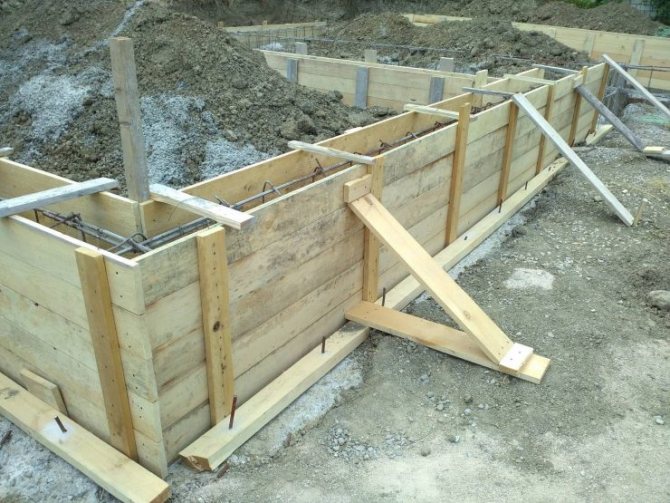

For each type of structure and the types of their bases (foundations), a certain type of formwork and its construction technology are used. In construction, there are two main types of such structures - temporary and permanent. In addition, they are classified according to purpose, design features, and materials used.
In construction, it is practiced to pour a foundation without formwork, directly into a trench dug in the ground, but the quality and durability of such a foundation cannot be guaranteed.
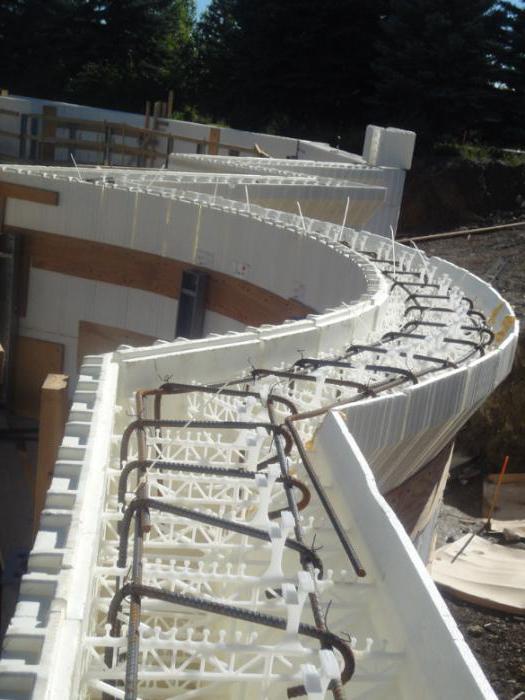
Advantages of permanent formwork
Installation of permanent formwork involves purchasing a ready-made kit for performing the work. All that remains is to assemble the structure and install it. This leads to a number of advantages that formwork of this type has:
- short deadlines for completing work;
- ease of installation;
- low weight of the structure;
- resistance to fungus and mold;
- fire safety;
- low cost.
Also, permanent formwork is both a layer of insulation and consists of foam blocks that are easily connected to each other. In this case, the inner wall is thinner than the outer one. Thanks to this, a high level of thermal insulation is achieved.

Advantages of monolithic flooring
To choose a building material for the construction of a building, you need to take into account many different factors, which will determine not only the construction time, but also the cost estimate. Installing floor formwork has many advantages:
- such a structure can be installed independently, without involving construction equipment;
- building material is cheaper;
- It is durable and therefore reliable in operation;
- installation is possible during the construction of buildings of various shapes.
In order to fill the floor, you need 3 components - a mixture of concrete grade B25 and higher, reinforcement, which is selected individually and depends on the type of building, and floor formwork. Concrete is needed to protect metal reinforcement.
The concrete slab must be at least 6 cm thick, because The strength and permeability of sounds depends on this parameter. The supporting reinforcement consists of iron rods that are bent upward in order to prevent cracking of the slabs near the wall.
When covering, a special belt is made, which is necessary for fastening the reinforcement. The reinforcement structure itself has a load-bearing role and folds in 2 directions.
Construction of permanent formwork
Installing wall formwork using permanent blocks is much easier than the traditional method.
Work begins with preparing the site and laying a layer of waterproofing. Blocks are simply placed on the foundation according to the principle of brickwork (with offset seams). This allows you to increase the strength (rigidity) of the structure.
To begin with, only one row of blocks is laid, then the reinforcement (overlapping). There are special grooves for this. The reinforcement is connected to each other by vertical wire. The following rows are laid out in the same way.
The blocks are attached to each other by simply connecting special grooves using light pressure. They begin to pour concrete mortar already on the third row of blocks.
There is one small secret in the work process. Walls will be more secure if the joints of the mortar layers remain in the middle of the block. To do this, the top row is filled to half.
Dismantling of formwork systems
Many developers are interested in when the formwork can be removed. It should be noted. That the period for dismantling the supporting elements is determined by the period of hardening of the concrete solution.

As a rule, dismantling work is carried out as soon as the poured concrete reaches at least seventy-five percent strength. If the temperature in the room is within fifteen degrees Celsius, and the humidity level is normal, then the formwork can be removed seven to eight days after the end of pouring, then wait four weeks for the concrete to gain its design strength. During this period, construction work is suspended or carried out at another site.
Stripping begins from the top point to the bottom, from the corner areas to the central point. First, all fasteners are removed - bolts, twists, etc. After this, you should move to the corners of the room - here the concrete hardens faster, the load forces are less than in the central part of the floor.
Then you need to lower the racks and dismantle the shields. The main feature when performing such work is the accuracy of its implementation. So that the formwork structure can be reused, it is cleaned of dirt, dried and stacked under a canopy for storage.
It is believed that a prefabricated formwork system manufactured in an industrial environment differs in quality and strength from a home-made structure. To minimize financial costs and reduce work time, floor formwork is rented using.
Features of removable formwork
We will consider the main points of formwork installation using the example of a removable collapsible structure. This type is most often performed by site owners without the help of professional builders.
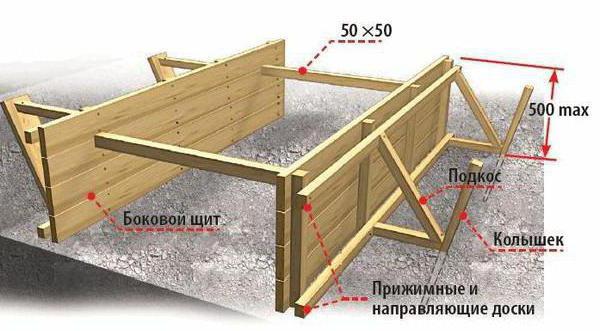
The formwork is installed from boards, bars, plywood and other sheets of wood. The main thing is that these slabs are level. All work begins with site preparation. The site must be completely cleared of foreign objects, debris, and so on. Next, the corners of the structure being built are marked with the help of bars. They will be the basis from which the rest of the measurements will be taken. In accordance with the dimensions, the formwork panel is assembled between the bars.
The finished panels are attached to the corner bars using self-tapping screws or nails. The fastening must be reliable. As the concrete expands, the pressure on the board will increase, which can lead to cracking of the boards. The main thing is that the block itself remains on the outside. Parallel to the assembled structure, another row is assembled at a distance from the future wall. The result should be a frame around the entire perimeter.
A layer of crushed stone or sand is poured into the finished formwork box. This will protect the solution from loss of moisture, which will go into the ground. The formwork installation technology provides for the protection of the wooden panel from the mortar leaking through the existing holes. To do this, the boards are covered with film or roofing felt, which are fastened with screws or staples using a stapler.
All work must be carried out taking into account the level. It is very important. At each stage, the evenness of the structure in height, length and vertical is checked (especially important). Two rows of shields must run strictly parallel to each other.
What materials are formworks made of?
In industrial construction, formworks made of metal (steel, aluminum) or expanded polystyrene are used. In low-rise construction or when creating small foundations, it is easier and more economical to create wooden structures. The only rule is to approach the choice of material responsibly. Experts recommend giving preference to larch or coniferous species:
- pine,
- spruce,
- aspen.
The material (boards) can be either edged or unedged, but specific requirements are put forward for the technical characteristics - humidity not less than 25%, thickness - from 20 to 50 mm, optimal width - 200 mm or more.
The boards for installing the formwork must be rigid so that you do not have to install many stops. A material that is too dry will absorb moisture from the concrete solution, which will negatively affect its performance characteristics, that is, the durability of the structure.
The boards can be used to make collapsible structures or panels. It is much more convenient to work with shields; they are easier to remove and install in another place. Boards are the main formwork material, but for its installation you will also need consumables. Their list must include self-tapping screws and tightening screws. If there is a high load on the structure, the nails may come out of the boards, and the foundation will not be even and not strong. In addition, you will need bars and polyethylene, which serves as a waterproofing material.
Basic elements of formwork
Removable formwork, which is assembled independently, consists of the following elements:
- A deck, which is a flat panel that encloses the entire form. The structure must be strong enough to withstand the pressure of the solution. Therefore, it is made from plywood or edged boards 4-5 cm thick.
- Scaffolding that supports the structure. They hold the walls, preventing the mortar from squeezing out the deck. Scaffolding is made from pine bars or boards (2.5-5 cm).
- Fasteners are all the parts with which all structural elements are twisted: wire, clamps, ties, hardware, and so on.
The deck is most often assembled from boards 15 cm wide, which are connected in several rows using nails (driven from the inside, bent from the outside) or self-tapping screws (they are screwed in from the inside). The distance between the boards should not exceed 3 mm. The shields are fastened together with additional strips.
A simpler option for making a deck is to use moisture-resistant plywood 1.8-2.1 cm thick.
Types of construction
The working surface, which is located between floors, can be filled in several ways, using removable and permanent formwork. If an apartment building with a large number of floors is being built, then a good estimate is included in such a building and, in most cases, mobile panels are installed using jacks.
If a person builds a house on his own, then a reliable but cheaper construction method is needed. In such cases, most often the installation of floor formwork occurs, which is carried out using more budget-friendly building materials.
The removable structure is made of wooden boards and consists of:
- thrust bar;
- spacers;
- embedded and covering panels;
- wire tie.
The design diagram can be easily found on the Internet. The non-removable design is more complex and includes more materials.
These structures are made from scrap materials:
- profiled sheet;
- waterproof plywood;
- tree.
If a large load is expected on the future floor, then the best material is corrugated board. Formwork made of wood or plywood is suitable for constructing the ceiling of the last floor, on which there is a non-residential attic.
Installation of formwork
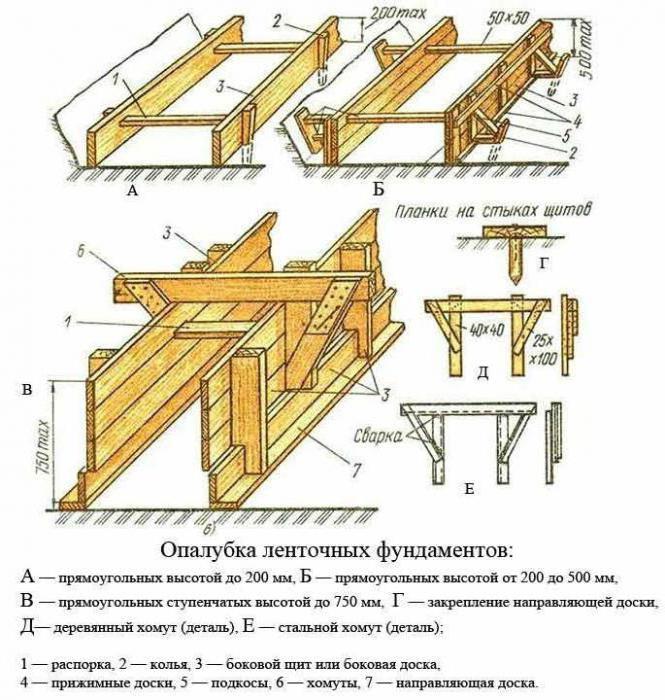
The frame will be installed level and level if the site is properly prepared in advance. It is marked using cords stretched between pegs. The sand cushion is filled in and compacted. If necessary, a pit is prepared.
Installation of formwork occurs in the following sequence:
- The perimeter should be marked with vertical guides (wooden blocks, metal corners or pipes).
- It is necessary to place the finished panels along the guides, maintaining the required distance between them (it is equal to the required thickness of the foundation).
- Securely secure the deck. Support it from the outside with inclined beams (1 strut for each meter of deck).
- Connect the panels together with 5x5 cm bars.
- Cover the inside of the formwork with film (roofing felt).
Foundations up to 20 cm high do not require serious construction. For them, bars driven into the ground are enough.
Monolithic flooring on moisture-resistant plywood
If you plan to build a very small house or the ceiling of a summer kitchen, then using steel sheets is impractical due to the high cost. In such cases, moisture-resistant plywood is used, which is also sold in sheets. Moisture resistance is an important factor of such a material, because... Damage caused by moisture when pouring concrete is unacceptable.
Installation work involves the use of materials such as plywood with increased moisture resistance, load-bearing wood beams and support posts. For example, for a span of 4 m and taking into account a beam pitch of 1 m, a section of 10x10 cm will be sufficient, taking into account a load of 150 kg/m².
Fastening occurs using self-tapping screws. The calculation of the reinforcement is specified in the project; it is secured using plastic clamps. Often, as an addition, waterproofing in the form of a film is laid.

Installation of wall formwork
The process of constructing wall formwork is more complex. In this case, small-panel and large-panel formwork are distinguished.
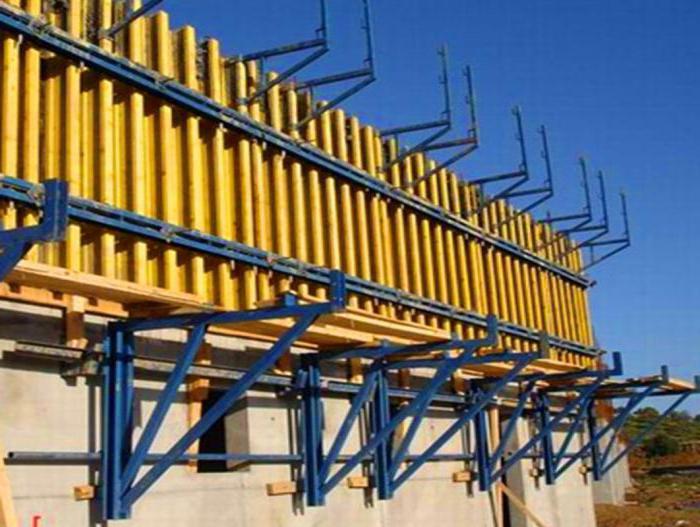

The first option is suitable for the construction of small buildings (country houses, utility buildings) and partitions between rooms. In this case, small-sized plywood panels are used.
Installation of large-panel formwork is typical for the construction of buildings with high heights. For work, use sheets of metal or large sheets of plywood.
To install the walls, prepare a foundation into which reinforcement is inserted. A two-row formwork frame is assembled around it. When using regular plywood, the joints are coated with glue or sealant. Currently, there is special plywood for formwork on the market. Its individual sheets are connected using the tongue-and-groove principle, which does not require additional sealing.
Horizontal formwork
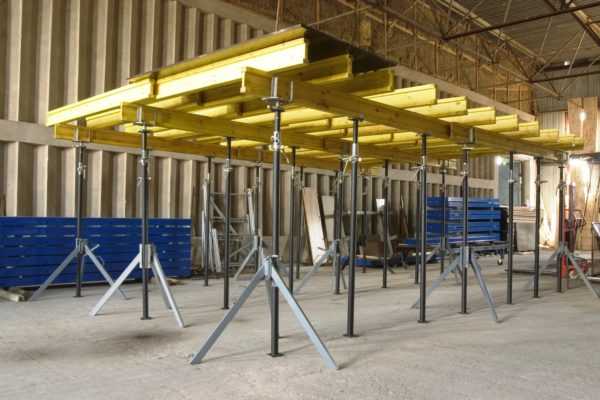

It is a multi-purpose structure, widely used in the construction of high-rise buildings. Often horizontal formwork is called floor formwork. With its help, you can cast reinforcing blocks, round, cantilever and rectangular ceilings and, directly, floor slabs. Finished structures have good sound and heat insulation and do not require complex preparatory work before finishing.
What parts does horizontal formwork consist of:
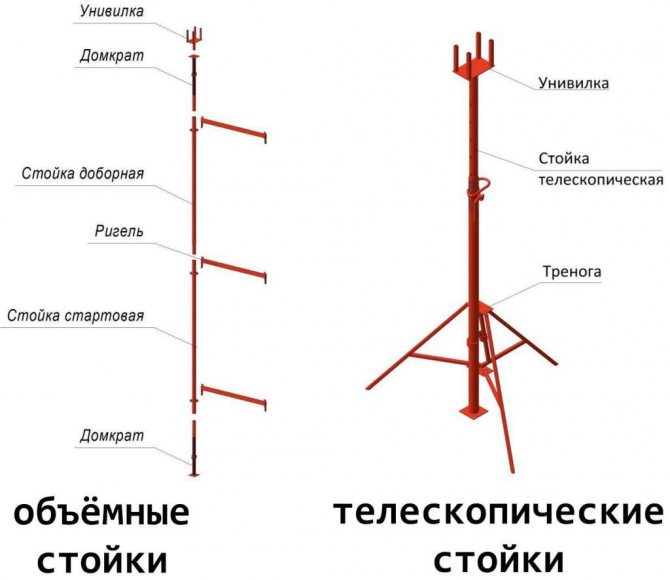
- support posts;
— uniforks;
- tripods;
- beams made of metal or wood;
— formwork panels.
If installed correctly, the result is a monolithic hingeless frame with high load-bearing properties. The key advantages of this type of formwork are low cost, the possibility of installation without the use of lifting mechanisms, ease of assembly and the ability to combine parts. It is worth noting that horizontal formwork is designed for a large number of working cycles and can be quickly dismantled. The most popular options are those made of galvanized steel or steel with a protective polymer coating. The panels are made of plywood with a high moisture resistance index.
In case of time restrictions for construction work, beam-transom formwork is used. Its assembly is carried out directly on site. The key advantage of such formwork is the ability to cast concrete structures of complex shapes.
What the installation process looks like for rectangular structures:
- Preparing the site and laying wooden flooring;
- Next, install the beams and crossbars, making sure to maintain an equal distance between them.”
- Starting from the outer beams, they are fixed to the crossbars using clamps. The distance specified in the project is maintained between the central beams.
- Sheets of moisture-resistant plywood are screwed to the fixed beams. The fastening elements are ordinary screws.
- To protect the structure from damage during construction work, timber is attached to its façade.
What the installation process looks like for corner structures:
- Construction site preparation;
- Installation of flooring and special corner crossbars;
- Fixing wooden blocks to crossbars;
- Installation of fastening loops on beams;
- Fixing the plywood deck to the supporting base using screws.
Types of floors
The installation of floor formwork depends on the type of floor itself. The following types of structures are distinguished:
- On large bowls. Used for structures with high heights. In this case, vertical posts, jacks, inserts, crossbars and other elements are used to connect individual parts.
- On wedge scaffolding, which is used for multi-story buildings. Instead of plywood panels, scaffolding is installed.
- On cup-type scaffolding. This type involves mounting a frame. The racks are connected to each other using the cup method.
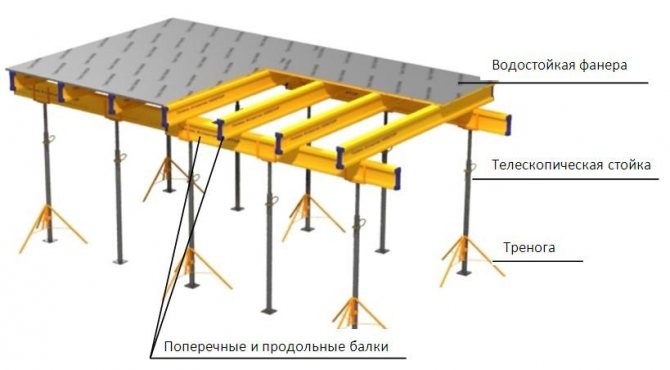
- On telescopic bowls. Suitable for cases where the ceiling height is less than 4.6 m. It is based on tripods that support the entire structure. Boards made of moisture-resistant plywood are laid on top.
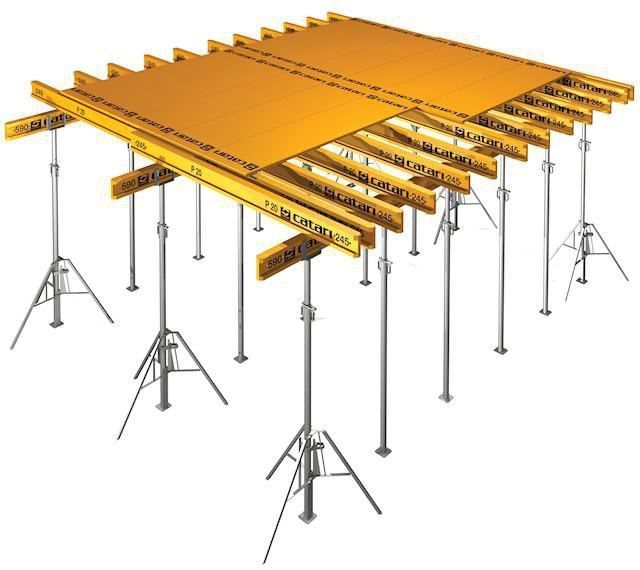
Composition and types
The composition is as follows: cross beams, telescopic posts, vertical perimeter panels, beam panels. The structure is fastened with ties.
Among the formworks for domestically produced floors, the most popular is the unified formwork. The formwork of the walls consists of panels with a width of 300 to 1800 mm and a height of one floor, as well as additional panels - corner and end. The shield consists of vertical trusses, horizontal beams and a metal deck. The installation of a monolithic floor is carried out after the walls of the room have been erected and they have gained the required initial strength. The structure is installed on telescopic racks, reinforcement mesh is laid in two levels, and concreting is carried out.
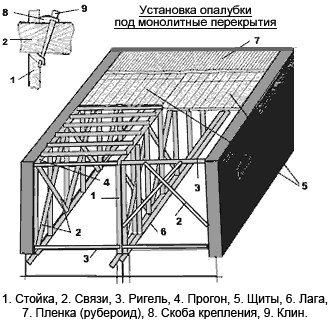
Scheme for installing formwork under a monolithic ceiling
The construction of a large-panel panel is carried out using the so-called solid formwork for floors, consisting of a set of modular elements that allow you to assemble a structure with a panel width of up to 5.6 m, a length of up to 12 m and a height from the parking level of up to 10 m. Stripping is carried out by reducing the height table supports. Subsequently, the structure is rolled out from under the ceiling and moved to another place. Rearrangement and installation are carried out with a “duck nose” traverse.
If you do not want to use wooden plywood, then reliable metal panels can be used as shields for the floor of the structure. They are smooth and even, so they fit as tightly as possible in relation to each other and are much faster to adjust horizontally.
Slab formwork
Currently, monolithic flooring is most often used. Using his example, we will analyze the process of installing formwork.
For formwork, vertical posts are used, connected to each other by crossbars. They are attached at right angles to bars running in the transverse direction. A plywood panel is laid on these cross beams, which is the bottom of the formwork.
To perform this work, the following materials are used:
- stand - timber with a cross section of 12-15 cm;
- crossbar and cross beam - edged board 16-18 cm wide and 5 cm thick;
- braces - board 3 cm thick;
- flooring – moisture-resistant (laminated) plywood 1.8 cm thick.
Before starting work, it is necessary to make accurate calculations. It is important to determine the required number of racks, the spacing of their placement and other indicators.
Application
Vertical wall formwork is used for surfaces of different areas, and its load-bearing capacity reaches 100 kN per square meter. Indicators are achievable through the use of a reinforced profile.
The same formwork can be used multiple times during construction work, so you can save money and not have to buy a structure every time you need to build an object. After use, simply disassemble it and fold it compactly. Formwork made of steel can withstand up to 1000 assemblies, and a structure made of aluminum can withstand three times less, about 300 assemblies.
Installation instructions for floor formwork
The work instructions include the following steps:
- Longitudinal bars are attached to the top of the racks, the second end of which is fixed to the wall.
- The second row is assembled in the same way. To do this, a 5 cm thick board is laid under the supports.
- Cross beams are laid in increments of 60 cm.
- Install the support posts (strictly vertically).
- The racks are connected to each other by braces.
- Sheets of plywood are laid on the cross bars, leaving no gaps.
- The ends of the ceiling are protected by masonry made of blocks or bricks.
- A frame is assembled from reinforcement. At the same time, if necessary, space is left for communications.
When all the work is completed, the concrete can be poured. The formwork is removed after 3 weeks.
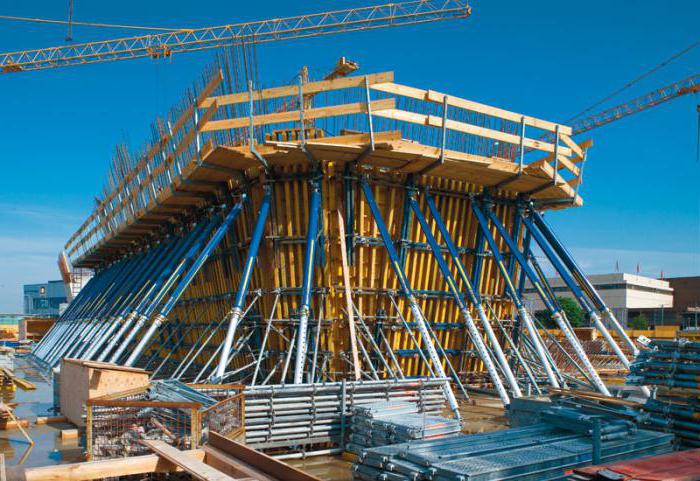

Formwork under the ceiling - design and installation principle
The formwork is arranged quite simply. It consists of a set of vertical supports that ensure the immobility of the longitudinal and transverse beams. Sheet material is laid on the beams. Along the perimeter of the sheet base there is a flange, the height of which corresponds to the thickness of the monolithic slab. The main task of formwork is to ensure the immobility of the concrete solution and maintain its shape until final hardening. The quality of installation of formwork elements determines the reliability and service life of the construction instructions.
Regardless of the design features of the formwork structure, installation of floor formwork is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- The support posts are installed in a vertical position in increments of 1-1.2 m.
- Transverse and longitudinal crossbars are laid on the supporting surface.
- The sheet material is attached to the support beams of the supporting frame.
- The edging elements are assembled and fixed around the perimeter of the formwork.
After completing these operations, the joint zones are sealed and the horizontalness is controlled. The installation process of plywood and metal profile formwork has its own nuances. Let's look at them in more detail.
Technology for manufacturing formwork using corrugated sheets
To construct formwork of a larger area, many developers use profiled sheets. Corrugated material marked H and NS is used. It is able to withstand increased forces from the mass of the concrete solution and the weight of the reinforcement cage. The tight fit of the profile sheets allows you to reliably seal the formwork. The corrugated surface of the material provides additional reinforcement to the structure.
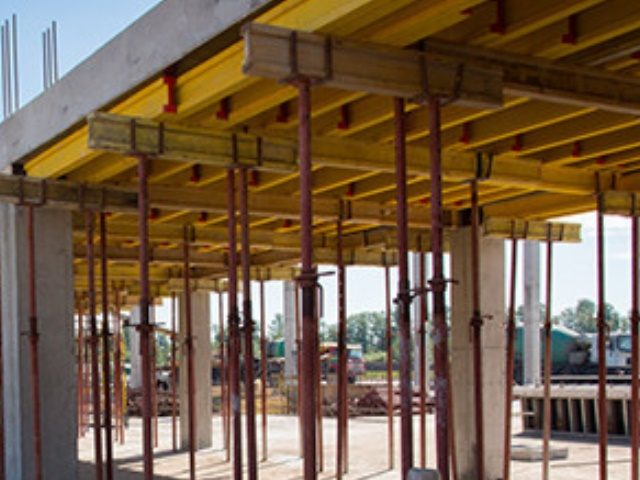

The reliability and duration of operation of the construction instructions determines the quality of installation of formwork elements
Observe the following procedure when installing formwork from profile sheets:
- Fix the supporting elements vertically.
- Lay and secure the longitudinal crossbars.
- Attach cross beams to the beams.
- Place profile sheets on the frame.
- Attach the corrugated sheet to the supporting frame.
It remains to check the reliability of the assembly and the horizontality of the structure, as well as seal the gaps. To concrete a monolithic floor, a reinforcement cage should be placed in the assembled formwork and the concrete mixture should be poured.
How is formwork installed using moisture-proof plywood?
When constructing formwork for pouring interfloor ceilings in private houses, it is advisable to use plywood sheets. Using plywood instead of expensive steel allows you to reduce costs. It is important to use moisture-resistant plywood. The use of plywood material with additional lamination will make it easier to dismantle the sheets after the concrete has hardened.
The procedure for installing plywood formwork elements is similar to assembling a formwork structure from corrugated sheets:
- First, wooden beams with a cross section of 10x10 cm are installed.
- Then the transverse and longitudinal beams are installed.
- Structural elements are connected using fixing elements.
- Sheets of plywood are laid and fastened with self-tapping screws to the supporting frame.
- Plywood blanks for edging are cut and attached along the contour of the formwork.
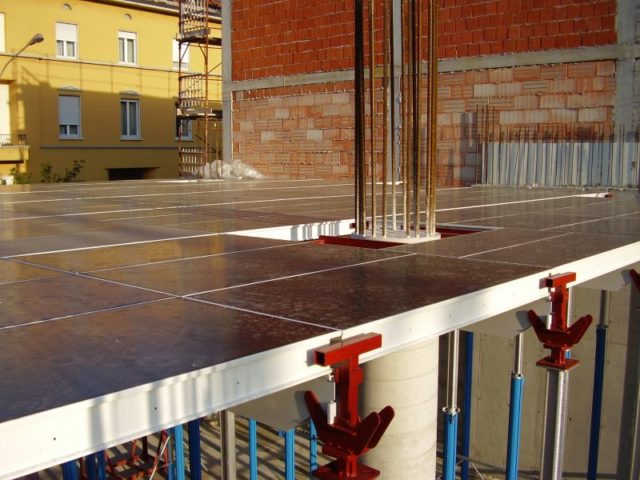

Attention should be paid to the absence of gaps in joint areas and corner areas, as well as between plywood sheets.
The cracks must be filled with foam. When carrying out work, pay attention to the reliability of fixation and horizontality of the formwork. To facilitate the dismantling of plywood panels and to prevent the plywood from absorbing moisture, the surface of the formwork is covered with plastic film.
Basics of vertical formwork design
The main component is the frame shield. It is manufactured from steel or aluminum frames using formwork boards. The frame is a hollow closed profile using shaped corrugation. Using the frame, several elements are fastened into a single structure, and the ends of the formwork slab are also protected from damage of various kinds. In order to increase the load-bearing capacity of the structure and facilitate installation, metal frames began to be made from closed profiles. This will allow for the alignment of modular elements. Vertical formwork has high rigidity, which is achieved by using a metal frame with ribs made of metal pipes. In addition, the structure is complemented by waterproof plywood 18 millimeters thick. To strengthen the walls, the formwork has special holes designed for attaching tie rods. Thanks to this possibility, it is possible to mount opposing panels using screeds with a pitch of 10 mm. This reduces the number of shields used in a set, and therefore reduces costs. The service life of vertical formwork may vary, since the indicator depends on many factors: • Protective lubricant; • Quality of cleaning of the structure; • Mounting quality. If all the rules for using the structure are followed properly, then it can last for quite a long time. Currently, manufacturers create formwork panels of various sizes. The width can vary from 200 to 1350 mm, and the height from 1350 to 3300 mm. To fasten several structural elements, various components are used - connectors, clamping rail, universal and quick-release clamps, anchor rods, superplate nut. Quality Standards Vertical formwork must comply with the following:
- GOST R 15.201
- GOST 380
- GOST 4784
- GOST 8617
- GOST 22233
- GOST 380
- GOST 14637
- GOST 16523
- GOST 2.601
- SNiP 3.01.01
- SNiP 12-03











