Even the area near the stairs can be turned into a sleeping area
Do not believe those who claim that installing a basement floor in a private house is more expensive than an above-ground floor. Its advantages are obvious: due to the strip foundation, which acts as walls, the cost of wall material is reduced. In the recessed part, the walls do not require external finishing, which also provides good savings.
Plus, the installation of a boiler room in the basement allows you to concentrate all the rooms into which water and sewerage are required. And this, in turn, makes it possible to minimize the cost of installing utility lines. We think that the above arguments are quite enough for you to pay attention to the option with a basement when choosing a house project.
Building regulations
First of all, in order to understand the intricacies of the purpose and arrangement of various underground premises, let us turn to the construction regulatory framework.
In this case, we are interested in the following documents:
- SNiP I-2 Construction terminology;
- SNiP 01/31/2003 Residential multi-apartment buildings.
These regulatory documents define all types of underground construction. It should be noted that all of them are tied to the planning level of the ground, which is essentially the ground level on the border of the building's blind area.
On a note! The planning level of the ground in graphic images is usually indicated by the abbreviation UR.Z. - ground level.
The photo shows an example of the designation of the ground level in the drawing
So, we are interested in definitions of such floors as:
- underground;
- basement;
- basement
Separately, we will analyze the definition of a plinth as part of a wall.
Terminology
We did not arrange the concepts randomly. Considering the rooms in this order, we will rise higher and higher above the ground level.
The definitions of floors given below are given exactly as they are prescribed in SNiP 01/31/2003:
- Underground - a floor with the floor mark of the premises below the planning mark of the ground level for the entire height of the premises;
- Basement - a floor with a floor surface level below the planning level of the ground by half or more of the height of the premises;
- Basement - a floor with a floor surface level below the planning ground level by less than half the height of the premises.
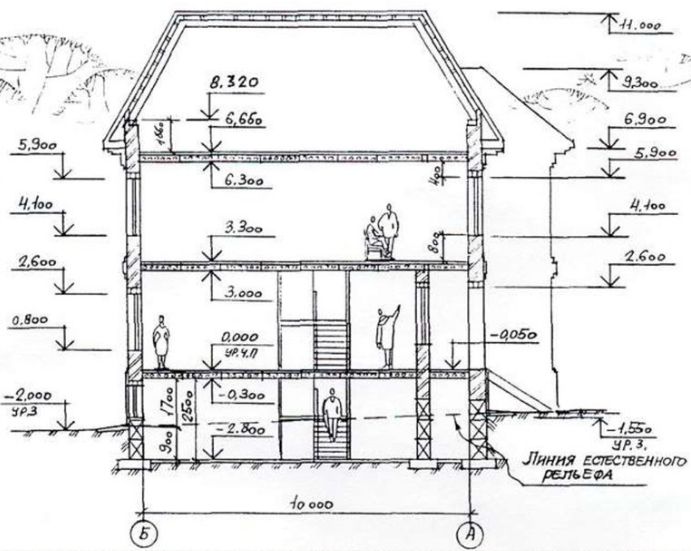
Let's look at everything in detail and understand how the ground floor differs from the basement or underground.
Schematic representation of the wall in the section of the basement and basement
Device
In order to get a completely or partially underground room, you will have to lay one of two types of foundation:
- recessed tape;
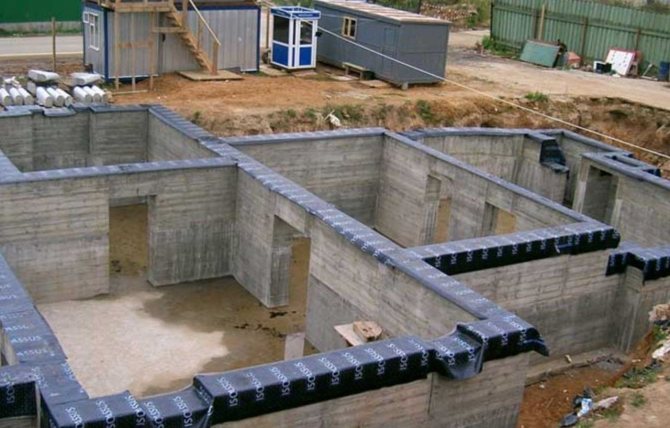

A buried strip is considered a cheaper base for the construction of a building with a basement.
- monolithic slab with ribs up.

Monolithic slab is the most practical foundation for underground premises
In both cases, the instructions for constructing a basement are almost the same:
- a pit is dug to the required depth;
- its bottom is carefully compacted;
- formwork is installed;
- a sand and gravel cushion is filled in;
- reinforcement is laid;
- the solution is poured.
Regarding our topic, it should be understood that a strip foundation is certainly cheaper, but the resulting floor will also be a dirt floor. Depending on the planned use of this room, if you have to install a solid floor, you will come to the price level of a monolithic slab, but will lose at least a month in time. So, the savings are questionable.
You can learn more about the foundation structure of a private house with a basement by watching the video in this article.
Types of socles
It is customary to use one of the separate types of plinths when constructing a finished project:
- Not buried in the ground. We are talking about structures that are buried no more than one meter into the ground.
- Partially recessed. Here we are talking about structures, half of which are buried in the ground.
- Recessed structures (a structure that is more than half buried in the ground is recognized as such.
The basement is also distinguished by the presence of a different exterior finish from the entire building as a whole. The basement does not contain such a distinction, since it goes completely deep into the ground.
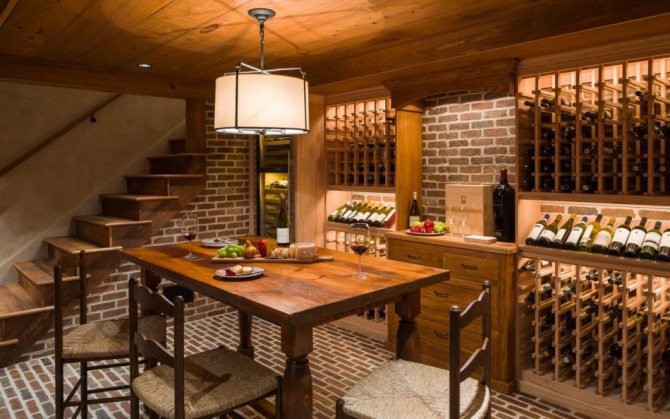

Use the basement and basement for wine storage
When constructing a structure, special attention is paid to external and internal waterproofing so that moisture does not penetrate into the room. Additionally, for this purpose, special groundwater drains are made at the sites.
Completely or partially underground
Let's start by looking at all the types of premises that interest us from the point of view of their location. Very often, the underground floor is considered a basement, and the basement is called the basement.
- Probably, there is nothing terrible in this confusion until the determination of the purpose of the premises in the BTI passport begins, and the price of the issue becomes clear.
- Depending on the status of the underground premises, it may be included in the taxable area or not taken into account as utility premises.
- Tax rates may change, but the type of underground structure of a building is a fairly stable concept.
On a note! As a result of the difference in relief on the site, the lower part of the building on one side can be defined as a basement, and on the opposite wall as a basement.
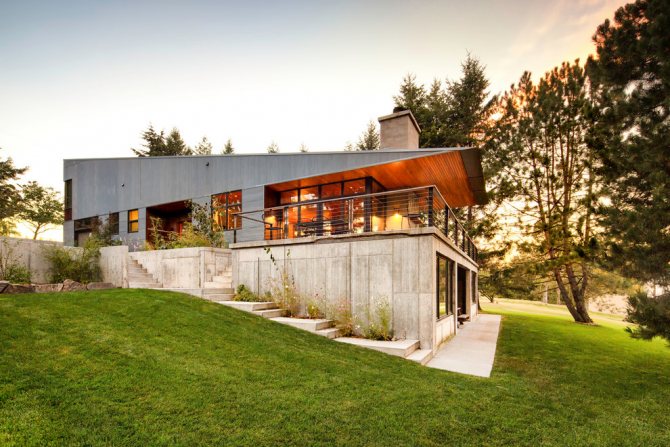

In areas with complex terrain, the same room can be defined differently from different sides of the house
100% underground
This type of premises is now quite rare in private construction, since the use of such premises can be very limited. But in multi-storey standard buildings, more and more often houses have at least one, and more often two, underground floors. Their area usually contains parking lots and storage rooms.
We look at this definition to understand that a basement is not an underground floor, although most of it is below ground.
Important! A room is considered underground only if its entire height is below the planning level of the ground
50% or more
If half or more of the height of the room is located underground, then this element of the building is a basement. Let us immediately clarify that when we say “basement floor,” we also mean the concept of basement.
There is no difference between these terms. And this is the difference between a basement and a ground floor, but more on that later.
Basement floors can be used:
- for laying intra-house communications and pipelines for various purposes;
- for installation of water or gas heating equipment;
- as a vegetable storage;
- like a garage or storage room.
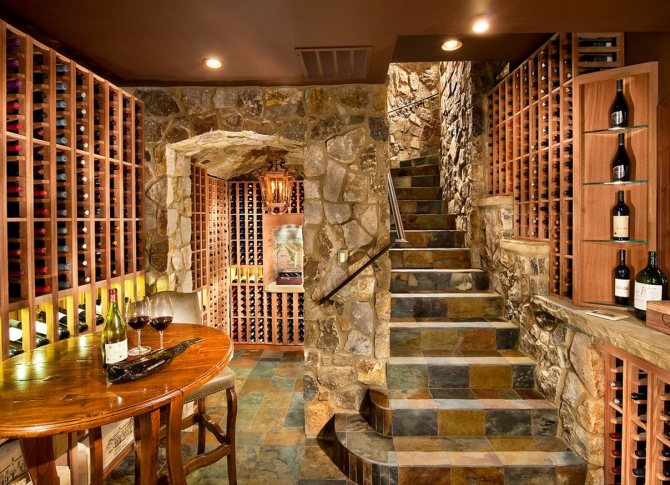

The absence of ultraviolet radiation and constant low temperatures make the basement an ideal place for storing fine wines
The scope of use of the basement is limited to economic needs, since as a result of its location, even if the basement has windows, they are very small, which cannot provide abundant daylight into the room. It is this fact that can save lives in an emergency: a basement can serve as an excellent shelter from a hurricane or tornado.
Often the basement is not located over the entire area of the building, but only in part of it. The thickness of basement walls depends on the material used for construction and the planned weight of the building, since these are essentially foundation walls.
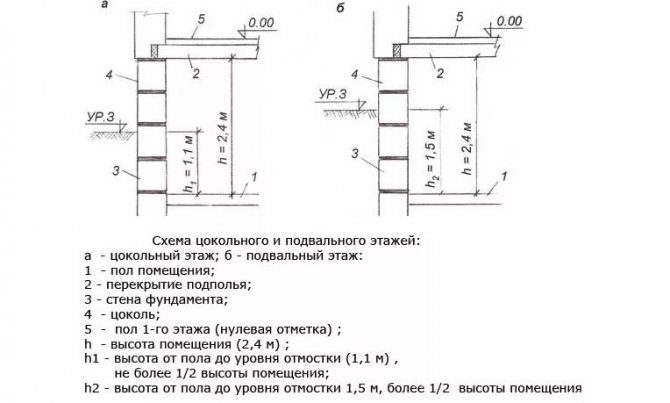
The height of the basement depends on what it is planned to be used for:
- up to 1.8 m cold underground for storing vegetables;
- 1.8 - 1.9 m laundry rooms, storage rooms, etc.
- 2.2 - 2.4 m relaxation rooms, saunas, billiard rooms, gym.
On a note! If you plan to build a house with an attic with your own hands, then when obtaining a building permit, it is better to indicate a basement height of less than 1.8 m. In this case, the project is not required to undergo an examination.
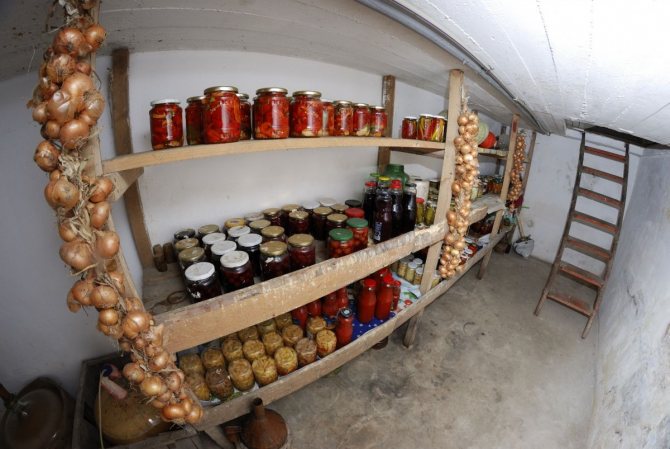

A small basement with a ceiling height of less than 1.8 m is quite suitable for storing preparations for the winter.
50% or less
Above we gave a definition of what a ground floor is, and now we will answer the question: how is the ground floor of a building determined, and we will separate 2 concepts:
- base;
- ground floor.
So, as already mentioned, the basement and the ground floor are not the same thing, although in everyday life, when we say basement, we usually mean the floor. What is the basement of a building? This is the lower floor of the building, which is half or more above the planned ground level.
Basement floor: definition SNiP 01/31/2003 - a room in which the floor mark is half the height or less below ground level. Based on the terminology, we see that the difference between the ground floor and basement is at least the height of the above-ground part.
On a note! Very often, people looking at offers to purchase housing have a question: what is the basement floor in an apartment building? The same as everywhere else, with one clarification. In multi-storey buildings, according to SNiP, residential premises cannot be installed in the basement.
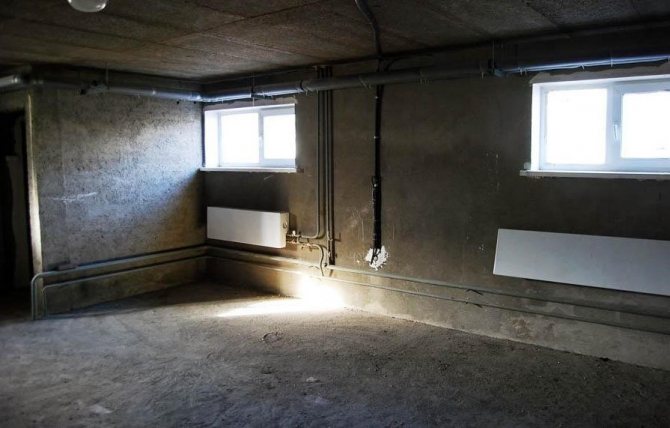

Basement premises of high-rise buildings are usually allocated for organizing various types of services and are rented out
What is a base? This is the lower part of the external load-bearing wall of the house, directly resting on the foundation, i.e. part of the structure that bears the main load due to the effects of high humidity, temperature changes and various mechanical shocks.
Thus, from the point of view of the structure of the building, the basement and the ground floor are two completely different concepts. The function of the plinth is to enhance the hydro- and thermal protection of the first floor of the building. And the fact that the superstructure allows you to create an additional floor inside is a pleasant bonus.
There are 3 types of base:
- Protruding, that is, the width of the basement walls is greater than the width of the load-bearing walls of the building.
- Equal level, the most popular option, but the least effective.
- Sunken, displaced inward by 5–8 cm relative to the wall of the house.
On a note! The option with a recessed base device is considered the most effective in terms of price-practicality ratio. Without requiring an increase in the estimated cost, it protects the building to the greatest extent.
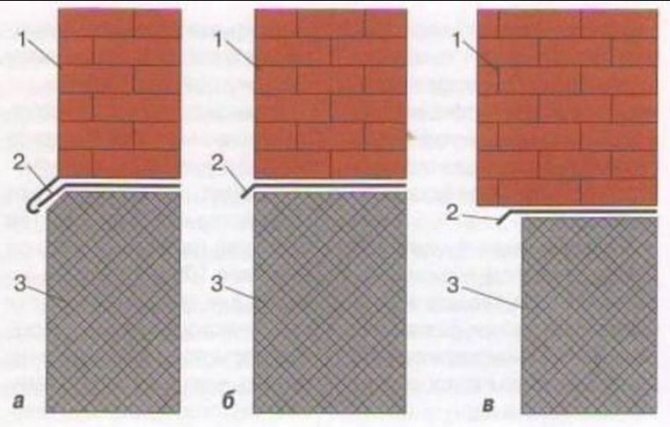
Various forms of the base: a – protruding, b – equal-level, c – recessed
Base design
Often, basement areas are called a plinth, but this definition requires the presence of the following room arrangement:
- Finished flooring. Often during construction a concrete screed is specially laid.
- Walls of the building. These elements are formed with the help of the foundation and are load-bearing for the entire structure.
- Small window openings that provide sufficient air ventilation inside the structure.
- A ceiling designed as a ceiling that separates, as in the case of a basement, the basement from the living area.
Based on these points, you can already draw conclusions for yourself what the difference is between a basement and a basement. In addition, it is unusual here for the structure to be completely buried in the ground.
Important. Often, when arranging a basement, an external foundation is used, which protrudes beyond the general boundaries of the entire building being constructed.
General and difference
It is necessary to know what the basement floor of a building is and how it differs from the basement even at the design idea stage. Such knowledge will help you correctly formulate the functions of the underground floor and lay out the right project. Let's reduce the similarities and differences between the basement and the basement to several points.
Similarities
There are obvious similarities between the ground floor and basement - both rooms are partially below the planned ground level.
In addition, they are united by:
- Functional focus. Despite the fact that in private construction the rules are sometimes violated, in a typical development the possibilities of placing utility rooms on the ground and basement floors are almost the same.
- Construction technology. In both cases, it is necessary to lay external waterproofing material and install natural or forced ventilation systems.
- During construction, similar moisture-resistant materials are used to build walls.
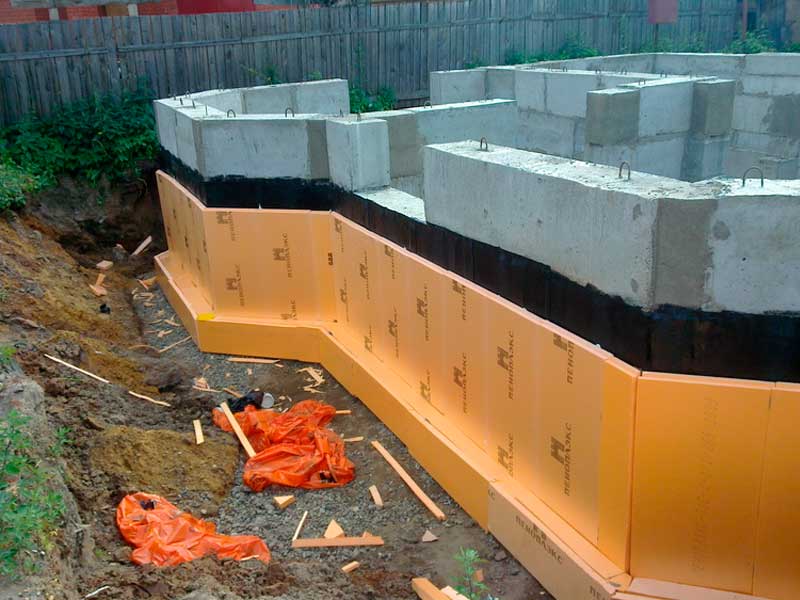

The technologies for constructing the ground and basement floors are almost the same
Differences
The main subtleties and differences are related to the structure of the basement - that is, the superstructure over the foundation walls, and not to the structure of the basement premises. If we conditionally combine these 2 concepts, we can ultimately conclude the following.
What is the difference between a ground floor and a basement?
- The basement, unlike the basement, is not part of the foundation walls.
- The basement superstructure raises the level of the first floor, which significantly improves the hydro- and thermal insulation of the first floor.
- The ceiling height of the first is usually higher.
- Possibility of installing almost full-fledged windows.
- The basement is located around the entire perimeter of the building, which means it is located under the entire area of the house.

The height of the basement allows you to arrange almost full-fledged window openings
Features of the arrangement of the basement floor
When improving this building element, you may encounter a number of features:
- there is no need to fill window openings due to their absence;
- entry requires installation of a door or hatch;
- At the entrance, a staircase for descending must be installed;
- it is necessary to remove the ventilation system through the roof;
- the floor is usually made of ordinary sand mound;
- there is no natural light, which requires appropriate wiring.
The scheme for landscaping the basement is different and includes other nuances.
Important. The definition of “basement” is inextricably linked with the concept of underground (there is always coolness, high humidity and lack of natural light).
How is the purpose different?
In general, the purposes of these structures differ significantly:
- Basements are usually used as storage, as well as for placing a heating system and distributing energy resources.
- Basement floors are rarely used for utility purposes. Usually there are additional living spaces or other comfortable rooms.
It is not advisable to confuse the definitions of the structures in question, since they differ not only in arrangement, but also in purpose.