The reliability of any building depends on the strength of the foundation.
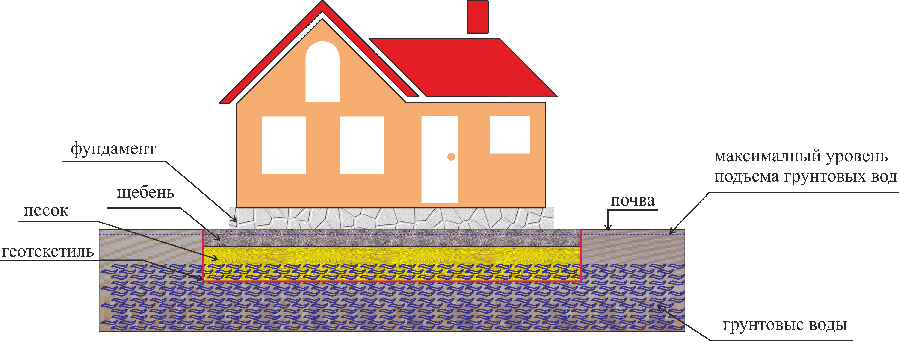
To strengthen its load-bearing properties, protect it from siltation and the negative effects of groundwater, waterproofing materials are actively used in construction.
One of them is geotextiles, which is widely available in the market. Western construction companies have long appreciated its effectiveness. Geotextiles are made from polymer materials and are distinguished by their technical characteristics and scope of application.
Purpose of geosynthetic material during foundation construction
Waterproofing of building structures is one of the important elements of protecting buildings and structures from environmental influences. Waterproofing of all types of foundations deserves special attention in this matter, because contact of moisture with reinforced concrete or metal certainly leads to a decrease in the performance characteristics of foundations.
Geotextile is a thermally treated fabric made of polyester fibers that has all the necessary functions to protect the base from water and chemical reactions.
Advantageous characteristics of the material:
is durable (up to 50 years);- does not absorb soil moisture;
- resistant to temperature changes in the range from –60 to +100 °C;
- not susceptible to the formation of fungus and mold;
- prevents plant roots from germinating;
- protects the foundation from rodents;
- environmentally friendly raw materials.
Geotextiles are effective in the construction of slab foundations on various soils:
- Sandy ones, which, despite their high load-bearing capacity and low degree of heaving, are permeable to groundwater.
- Clay ones are too mobile to guarantee the durability of the structure, so they need reinforcement.
- Peat - they represent too weak a foundation and in this case the builder needs to recreate a stable support.
Functions of the canvas
The purpose of geotextiles for slab foundations is as follows:
- Reinforcement – makes the base of the structure elastic and at the same time is responsible for the distribution of loads. Reinforcing geotextiles several times increase the bearing capacity of the soil under the base of the foundation. If you plan to build a complex structure on a slab with uneven pressure on the base, then it makes sense to use geotextiles with a density of 350 to 600 g/m2.
- Drainage - removes groundwater from the base of the foundation, preventing moisture from penetrating into the structure of materials above the geotextile. To serve as a drainage barrier, the material must have a density of at least 200 g/m2.
- The separation of the cushion and the soil prevents the process of siltation of sand from developing, as well as the mixing of various materials with each other. As a result, the pillow does not lose its drainage properties and load-bearing capacity during operation.
Types and properties of geotextiles
Geotextile was invented to protect against soil destruction in the form of landslides, soil shifts, and landslides. Gradually, the versatility of the material gave it wide application in areas of construction and economic importance.
Kinds:
- Woven - high modulus polyamide threads are intertwined with polyester, resulting in a very durable fabric.
- Non-woven - has several varieties according to the production method. The fabrics are needle-punched, thermally bonded and hydraulically bonded.
Properties:
- Excellent water throughput.
- UV resistance.
- Frost resistance.
- Neutrality to aggressive environments, does not decompose under the influence of time.
- Resistance to mechanical damage.
- Resistant to pressure loads.
The marking of the fabric indicates the density and scope of application, but usually there are no additional instructions on which side to lay the geotextile to the ground. Woven fabrics have similar surfaces, allowing water to pass through equally on both sides. Non-woven fabrics have a rough or shaggy front surface and a smooth back surface. It is logical that the rough one will have greater resistance to silting.

Excellent reinforcing and drainage substrate Source gidroizolyaciya22.ru
Criterias of choice
Types of geotextiles differ in composition and technical characteristics. The choice of material is directly related to the specific design conditions in each specific case.
In this matter, an individual developer should pay attention to such characteristics of geotextiles as flatness, fabric thickness, elasticity, etc.
By density
The density criterion is the most significant indicator on which the effectiveness of the material depends on the given conditions:

geotextiles with a density of 150 to 200 g/m2 are suitable for draining groundwater and installing drainage layers;- fabric with a density of over 250 and up to 300 g/m2 is strong enough to reliably separate the soil base from the sand and crushed stone foundation cushion;
- high-density geotextiles (from 350 g/m2) are capable of ensuring uniform distribution of loads on the soil through the foundation slab under brick and other heavy houses.
By thickness and other parameters
The degree of compressibility, as well as the wear resistance of such a substrate under the pressure exerted by the structure on the ground, depends on the thickness of the geotextile. The optimal value for slab foundations is from 1.8 to 3.8 mm.
When choosing a material, they also pay attention to moisture resistance, susceptibility to mold, elasticity and other characteristics specified in the specification for the product.
The better the performance, the more expensive the cost of the material , so you first need to study the design conditions, and then determine the technical tasks that geotextiles must cope with.
The video will tell you how to choose geotextiles:
Scope of application
Modern material is used in various areas of construction and landscapes. The canvas does not require additional equipment when rolling and laying. It is cut with ordinary scissors, and can be fastened with double-sided tape or staples. Service life up to 30 years.
Areas of use:
- Construction of park areas, roads and sidewalks. The strength of geosynthetics and water permeability prevent the bedding from silting and provide additional elasticity.
- Geotechnical objects - installation of drainage systems, combating the destruction of slopes from erosion. The wrapped drainage pipe does not become clogged with small fractions of soil and does not require cleaning.
- Landscape objects – lawns, ponds, swimming pools. The elastic bedding prevents soil subsidence, making the foundations stable. When laid in the pool, it will protect the waterproofing layer.
- Destruction of weeds in gardens (growing strawberries and other crops). Laying geofabric allows you to fight even sow thistle and wheatgrass, weeds that are practically resistant to herbicides.
Geotextiles must be laid on the ground with the side that will allow water to pass through and not allow weeds to run free.

The process of laying geofabric Source ytimg.com
Which one do you need?
Geosynthetic material is laid on the compacted bottom of the pit under the slab foundation. As a rule, the surface does not have bends or kinks, so it is advisable to use heat-pressed film, which has an affordable price and sufficient strength within a density range of 200 to 250 g/m2.
If the project is to build a two-story house with massive walls made of heavy material, then it is advisable to purchase geotextiles with a density of 350 g/m2 to evenly distribute loads along the base of the sole.
Progress
- Before the installation begins, the rolls are delivered to the production sites.
- Then the brought material is distributed along the length of the structure to a distance that should be approximately equal to the width of the canvas. It should be located across or along the embankment. According to technology, the most convenient option for placing material is longitudinal. Although it will not be able to provide the same strength of the material across the entire width. Nevertheless, this indicator is considered mandatory when installing a reinforcing layer, unless the base is considered weak.
- Products are rolled out manually during operation. The workers press the first meters of it with two anchors, which should be located at the edges. During further rolling, tensioning of the products and high-quality leveling are performed. Then the material is secured every 15 m, also using anchors.
- If the products are placed under the foundation structure, then an overlap of approximately 0.5 m is required, and there should be no connections on it. But if the products were connected, then the size of the overlaps can be reduced.
- When working in difficult soils, the blades can be connected in parts, sometimes completely. If the sequence of work was carried out correctly, starting from the moment of the preparatory process, then the protection of structures will be of high quality and long-term!
Laying rules
Laying geotextiles should not cause any difficulties for an individual developer if he follows these recommendations:

Before work, the bottom of the pit must be sufficiently compacted and have a flat surface without any construction debris.- The rolled material is laid out, avoiding folds.
- The strips of material should overlap with a margin of 15 cm or more. If the geotextile joints are soldered or stapled according to plan, then an overlap of 10 cm is sufficient.
- A layer of non-metallic material is laid on top of the geosynthetic material, and then thoroughly compacted using a special device. Until the bottom is compacted, crossing its surface by vehicle is prohibited.
Laying under the foundation
Geotextiles under the foundation are used in two main areas:
Protection of waterproofing and insulation from external influences
The dug trenches are covered with sand, compacting the base tightly. A cloth is spread on the sand that can withstand loads of 300 g/cm. Formwork is installed in the trench, and the walls are covered with the same fabric, sealing the joints with double-sided tape. Next, the reinforcing frame is installed. The next step is to pour the concrete solution and leave it until it hardens completely.
The formwork is removed from the hardened monolith and the canvas is checked for integrity. Accidentally damaged areas are glued.
Geotextile protection provides additional insulation from external factors - reduces heat loss through the outer walls of the foundation and prevents moisture penetration.
Features of use for blind areas
The blind area is a continuous contour around the house . Its function is to prevent rainwater and snow from seeping into the structure of underground structures. The blind area also protects the structure from soil movements under the influence of frost heaving forces.
According to the blind area construction technology, geosynthetic material is laid under a layer of non-metallic materials around the base. The edge of the film on the side of the house is placed slightly above the surface line of the blind area to ensure waterproofing of the foundation and plinth.
As a rule, an expansion joint is made in this place, which is then coated with hot bitumen or laid with a special sealing material.
Installation of an artificial reservoir
When constructing a pool or pond, geofabric is also used to protect the waterproofing. A base made of soil and small stones can damage the waterproofing layer. Therefore, the base of the bowl is compacted tightly and geotextiles are placed, which perform reinforcing and protective functions.
Next, a membrane waterproofing layer is applied. You can add more geosynthetics on top to make the base stronger. Next, work is carried out according to the design of the reservoir. A correctly calculated foundation at the beginning will subsequently delight the owners with a long service life of the pond or pool.
Popular brands
Currently, a wide range of geosynthetic materials is available to individual developers. Among the domestic brands the following are in demand:
- "Lavsan Geo" is an inexpensive geotextile made of polyester fibers with a density of 100 to 600 g/m2.
- "Avantex" is a budget option for geosynthetic material. Its advantage is that the width of the sheet is immediately made to allow for overlap.
- "Geospan" is a propylene material made from primary raw materials. Geotextiles of this brand are characterized by high strength and elasticity.
- "Stabitex" - the canvas is made entirely of polyamide, therefore it is resistant to stretching. Geotextiles of this brand are especially effective if the soil on the site is prone to movement and deformation.
- "Kanvalan" - Non-woven material made of 100% polypropylene, characterized by high strength. Widely used for the construction of foundations for heavy structures.
Geosynthetic materials from foreign manufacturers (Polyfelt, Typar, Fibertex, etc.) are in less demand because they are overpriced for the same performance characteristics.
Comparison of the cost of geotextiles from various manufacturers:
| Brand | Price, rub./m2 |
| Lavsan Geo | 15–44 |
| Avantex | 16–56 |
| Geospan | 25–56 |
| Stabitex | 28–80 |
| Kanwalan | 23–60 |
| Polyfelt | from 29 |
Briefly about the main thing
Geosynthetics significantly improve the strength and elasticity of the base, acting as a reinforcing coating.
Garden and landscape design work would take much longer without geotextiles.
It is much easier to grow strawberries if you first lay geofabric on the ground, and then cut holes and plant the seedlings. Water seeps through the fabric, and weeds cannot break through the dense, dark fabric.
For which side is the correct way to lay geotextiles on the ground, read the instructions for use in the roll labeling.
Ratings 0