The types of soils on the sites influence the choice of foundation for the building. A house will be durable and strong if it is built on a solid foundation. And the foundation, in turn, rests on the ground. Soil types vary in their composition and ability to hold water.
In construction terms, the word soil refers to the layer of earth directly under the foundation of a structure, which receives two types of influence. Firstly, these are all the loads from the structure, and secondly, this is the action of natural forces. Moreover, the first factor is much easier to take into account than the second.
To link a house project to a specific construction site, it is necessary to take into account a number of parameters, the most important of which are the type, composition and structure of the soil, its humidity and groundwater level, the amount of precipitation, and the presence of perched water. The depth of laying many types of foundations depends on the depth of seasonal freezing of the soil.
Studying the hydrogeology of the site should precede the choice of the type of foundation. This is especially important when building two- or three-story houses with basements, since protection from groundwater is not an easy task and requires significant material costs.

Characteristics and properties
The formation of loam occurs as a result of crushing and settling of rocks with a high quartz content. The natural material is more common than pure clay. Most often, formation occurs at the foot of hills, in the floodplains of rivers and streams.
Mining is carried out in an open way, directly from the surface of the earth. Due to the ease of destruction of this rock, the extraction method is extremely simple - just collect the soil using construction equipment. It is not uncommon for loam to be a by-product of the development and extraction of other natural materials.
Sandy impurities significantly changed the properties of loamy soil:
- Particle size distribution - depends on the particle size. There are clayey, sandy and dusty ones;
- Density is the ratio of the mass and volume of soil (kg/m3, g/cm3). Includes indicators: total density, density of the solid phase and skeleton. The density of the solid phase is a stable indicator that does not depend on humidity and air conditions. It is 2690-2730 kg/mʒ. Changes in the parameter occur upward with an increase in the percentage of rocky inclusions (crushed stone, boulders, pebbles). As organic matter increases, density decreases;
- Porosity is the ratio of pore volumes in the soil to the total volume of the sample taken. For loams, this indicator is in the range of 0.5-1 (fractions of one). Porosity can be expressed as a percentage. As the composition of organic matter increases, porosity also increases. It is higher in the upper loose layers of loam. This is one of the most important properties of loam; the shrinkage of the material depends on porosity;
- Plasticity is the ability to change shape under the influence of physical influence and its further preservation. This is one of the distinctive features of loamy soils. Tests are carried out with wet material. Plasticity is measured as a percentage or fraction of a unit;
- Fluidity is the ability to liquefy when oversaturated with moisture. In this state, the material loses the ability to take and maintain a certain shape. It is very important to determine the limit at which soil fluidity begins. Construction of foundations on such soils is difficult;
- Resistance to deformation - do not differ in particular strength. Loams are prone to plastic deformation, but not rapid destruction;
- The ability to swell is the ability to change volume when saturated with moisture. The more montmorillonite in the loam, the better it swells. If quartz predominates in the composition, swelling is reduced;
- Shrinkage —low-porosity, dense loams are less prone to shrinkage than those containing more organic matter;
- Heaving is the ability to change volume when water freezes, which expands in the pores of the soil when it freezes. Loams are heaving soils. This property is more pronounced in the upper looser layers, which contain more organic matter;
- Stickiness is a property inherent in loamy soil when moistened. At a certain point, the indicator does not increase, but falls due to the destruction of the connection between water, soil and surface. Loams are sticky materials;
- Water permeability is the ability to let water pass through. For loams, an indicator of 0.5 m/day means low water permeability;
- Water resistance - quickly get wet and erode;
- Bearing capacity - the drier the soil, the higher its bearing capacity.
Screw pile calculator
SERVICE COST CALCULATOR
COST: 0 rub.
Specify the cost when ordering
CALCULATE
X
The installation depth of the piles must be no less than the level of soil freezing - for the northern regions it is one and a half meters, for the southern regions - 1.2 m. If there are difficulties with screwing the piles, this will negatively affect the reliability of the entire building. Because of these features, pile foundations are extremely rarely installed on rocky soils.
Difference from sandy loam, sand and clay
According to its characteristics, loamy soil occupies an intermediate position between clay and sandy loam.
Sandy loam
Unlike loam, sandy loam contains a higher percentage of sand (up to 70%) and clay compounds - no more than 5-10%. The presence of a large amount of sand reduces the plasticity of the material and increases its water permeability (up to 3 m/day). Sandy loam is practically not subject to heaving, unlike loam. The bearing capacity of sandy loam increases with compaction and decreases with moisture.
Sandy loam
Sand
Sand is a fine-grained, loose rock formed as a result of the weathering of rocks. The content of clay particles is negligible (up to 5%). Unlike loam, sand is not plastic, is not able to retain water in its pores, and does not have sufficient density. The load-bearing capacity depends on the compaction. High filtration capacity - up to 10 m3/day.
Sand
Clay
Sedimentary rock is dusty when dry, but when wet it turns into a plastic mass. Minimal quartz content, small particle size in contrast to loam. When rolling out the cord or shaping it into another shape, the material does not form cracks.
Clay
Additional work
The main problem when building a house on heaving soils (including loams) is to build a foundation that can adequately accommodate the increase in soil volume during the cold season. The reason why all this happens is soil moisture. Therefore, when groundwater and surface water levels are high, it is necessary to arrange foundation drainage. It is best to think about this issue at the stage of foundation construction - this way the costs will be lower, and the efficiency of the drainage system will be much higher.
When the problem of soil moisture is solved, it would not be a bad idea to provide additional thermal insulation around the perimeter of the house. This is done in order to reduce the depth of soil freezing, thereby reducing the risk of soil heaving to zero.
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Classification of loamy soil
The main classification of loams is carried out depending on the soil density indicator. An important building indicator of soil—bearing capacity—depends on density. Depends on the amount of rocky or organic components:
- light loamy rock - sand content about 40%, plasticity 5-12%. Light loam contains only a third of the clay component and its characteristics are close to sandy loam;
- medium loamy soil - contains more than 40% clay. The soil is classified as hard-plastic, semi-solid;
- heavy loamy soil - clay makes up more than half of the soil volume. The characteristics of heavy loam are similar to clay, with the difference that the material is less porous and dense.
Another division of loams into types depending on the type of impurities in the composition:
- boulder - loam containing rock fragments of various diameters - from 10 cm. This can be crushed stone, pebbles, gravel, boulders, etc.;
- loess-like rock - loamy soils containing fine particles and carbonates. Like other loess, the rock is colored yellow. Yellow loams have less porosity and are less prone to shrinkage.
What is the predominant depth of groundwater and what does it affect?
Rocky type of soil is a solid solid mass, which is an ideal foundation for the construction of structures of any type. A site with just such soil is selected for the construction of heavy multi-story buildings. This is also due to the fact that natural rocky soils are waterproof, so such an indicator as the depth of groundwater is insignificant when choosing the optimal type of foundation.
See also: Catalog of popular plots in the Moscow region for the construction of a country house
Loamy soil deposit
Loam is extracted from the same quarry as other related rocks. They come in layers according to the degree of content of kaolin particles. Loam is located above the clay layer. During the extraction of loamy soils, each of them is developed separately, since it has a different set of useful properties.
Loams are one of the most common soils in the world. It is mined by most countries. This is due to the ease of extraction and wide range of applications of natural material.
Features of clay soil
Clay soils are soils that consist of 80 percent or more clay and a maximum of 20 percent sand. If you try to knead a lump of such soil in your hands, it does not crumble into grains, but is smeared, turning your hands red and molded. Clay is rich in various mineral compounds necessary for plant growth, but they practically do not enter the root system from dense soil, which is why clay soil is called greedy. It also has a number of other disadvantages:
- the soil is difficult to cultivate; in dry weather it is hard, like stone, and when wet it sticks to the shovel in a thick layer;
- due to the dense structure, air circulation deteriorates;
- the soil has low thermal conductivity and warms up slowly, so the seeds take a long time to awaken;
- during the rains and after the spring melting of the snow, the ground floats, there are puddles on the surface, but the moisture does not penetrate deep into the soil. Stagnant water prevents air circulation and causes acidification, and most cultivated plants do not take root in acidic soils;
- in the heat, a hard, cracking crust forms on the surface.

When clay soil dries out, it cracks
Process of extraction and transportation
Before starting the development of a deposit, exploration of the occurrence of rocks is carried out in order to determine their characteristics and the expected volumes of occurrence. After reconnaissance activities, the area is cleared of unnecessary layers of soil and vegetation.
The extraction process itself does not require special complex equipment. An excavator is enough. After being removed from its natural location, the soil is transported for processing. Often the enterprise is located close to the quarry. At the factory:
- grinding;
- sifting;
- mixing with chemical reagents depending on further use.
Which foundation is better to choose?
The construction of a private house on natural rocky soils can be carried out using various types of foundations:
- Recessed strip foundation.
This type of base is best used on soils that are not entirely, but only partially, rocky. With a deep strip foundation, the soil is first excavated, which includes digging a pit and leveling the area. After that, a sand cushion is laid, which is covered with waterproofing. Next, formwork, reinforcement and pouring of the base are performed.
This type of foundation is durable and reliable, but its use is only possible if the soil allows you to go deeper by at least 70 cm, and in the case of solid rocky soils it can be very difficult to go deeper than 50 cm.
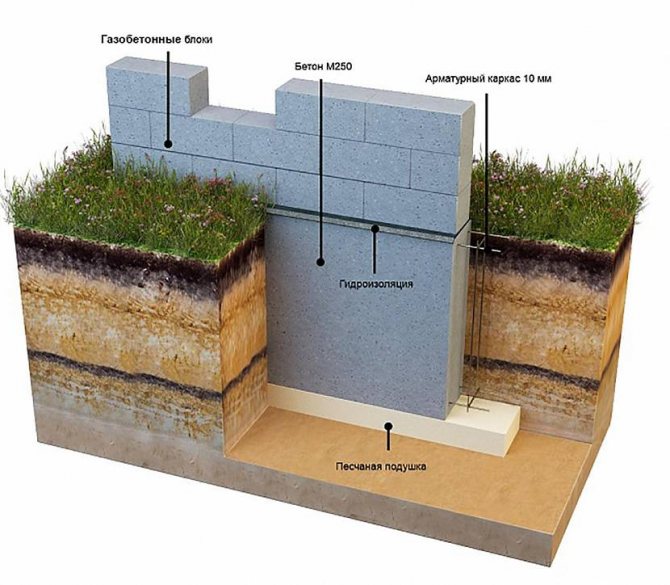
Recessed strip foundation Source ast75.ru
- Shallow strip foundation.
For such a base, it is enough to deepen the tape by only 30 cm, and the sand cushion may not be used at all. If the ground is level and rocky, you can even refuse to use a reinforced belt.
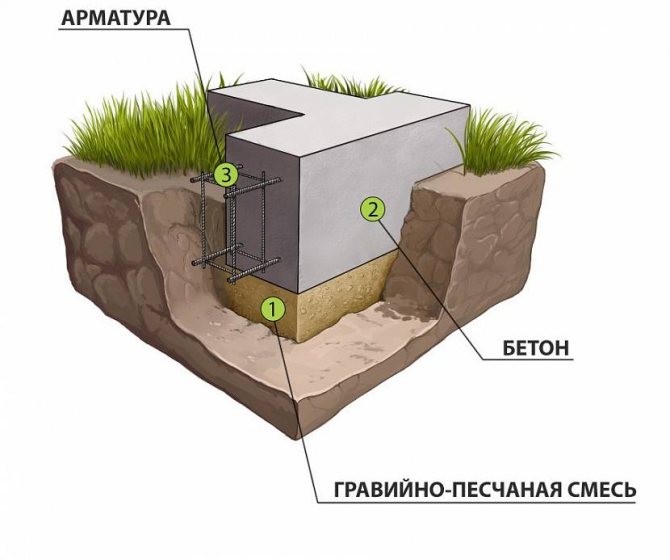
The use of a sand cushion is not necessary, but is not prohibited Source sk-angara.ru
Areas of application of loam
Loamy soils are widely used:
- Road construction;
- Housing construction;
- Production of building mixtures;
- Agriculture - production of artificial plant soil mixtures;
- Construction of complex engineering structures - the insulating properties of the soil allow it to be used in the construction of dams, dams, strengthening river coastlines;
- Landscaping - most often, loams are used to construct natural pools and landfills;
- Chemical industry . For example, the creation of inert utensils that are resistant to aggressive chemical compounds;
- Medicine - production of sorbents, cosmetics.
Determining the mechanical composition of the soil - test with water
The main types of soils are: light (sandy and sandy loam), medium-heavy (loamy), heavy (clayey). Determination of the mechanical composition is carried out using a test familiar to many. Moisten a handful of soil well with water, trying to obtain a thick paste-like consistency. Now take the moistened lump in your hands and try to twist it into a “sausage” and make a ring. The result of the experiment will tell you what type of soil you are holding in your hands. If the soil rolls up well and forms a tight ring, then the soil is heavy.
Determining the type of soil
If it rolls well, but forms cracks when twisted into a ring, it is classified as a medium type. And if it crumbles in your hands and it is impossible to make even a thin rope out of it, this means that the earth is light. These types of soils are water- and breathable, differ in density and moisture-holding capacity. Each of them is adapted for growing various cultivated plants, with an individual approach to care and feeding.
Methods for determining loam on your site
It is quite difficult to determine the composition of the soil by eye. But the possibility of growing certain plants depends on this indicator. Performing one type of foundation or another. There are several ways to determine the type of soil on a site.
Why can't you tell the soil by color?
Trying to identify loam by color often leads to mistakes. With this method, it is difficult to determine the number of clay particles in the composition. The color of the soil indicates not only the percentage of clay, but also the characteristics of the mineralogical composition. For example, the color of the earth is particularly influenced by the proportion of iron or aluminum it contains.
Overmoistening leads to the formation of a gley horizon, which has a bluish color. This color is the result of a reaction between iron and clay minerals. The rusty color comes from a combination of iron and manganese. This color does not indicate the presence of a large amount of clay and makes the soil toxic to plants.
Sandy loam often repeats the color of loamy soil, but the material itself has completely different characteristics.
Rolling into a cord or ring
A simple method that every site owner can use. Based on the definition of a material feature - plasticity. Determination algorithm:
- take a small amount of soil in your hand;
- moisten it with a spray bottle to achieve a dough-like state;
- try to roll the resulting mass into a cord;
- try to roll the cord into a ring.
Conclusion - if the mass rolls out into a cord that can be rolled into a ring, it is loam. Depending on the type of loamy soil, the ring will be weak (light) or dense, but with cracks (heavy).
If the resulting ring does not have cracks along the edges, clay predominates in the area.
Touch test
Less informative way. You will need to wet your hand with water and rub some soil between two fingers. The particularly oily nature of the soil indicates that it is clay. Almost only grains of sand indicate that sandy loam predominates in the area.
Loam is an oily mass with noticeable inclusions of quartz sand.
Laboratory method
The most informative and accurate research method. You will need:
- a measuring cylinder into which a portion of the soil is added;
- dilute with water and shake thoroughly.
Conclusion - increased turbidity of the suspension indicates the presence of clay particles in the composition. In the case of loam, the sandy component of the soil will settle to the bottom. In the case of sandy loam, there is practically no turbidity; almost all of the soil quickly falls into sediment.
Use of rock soil in construction
Here the rock is used for the following work:
- Strengthening the soil under the foundation
- Raising the level of the site
- Production of low grade concrete
Next we will dwell on each point in more detail.
Strengthening the soil under the foundation
The rock is considered the most reliable foundation. It forms a thick layer that prevents deformation of the foundation. For example, during the construction of multi-story buildings, piles are driven into the ground to construct the foundation. They fit firmly into the rock mass and ensure the reliability of the structure.
In private low-rise construction, this method is practically not used - it is too expensive. But it happens that there is weak soil under the future foundation. In any case, it will have to be strengthened. This is where the rock comes in handy.
To strengthen, the top fertile layer of soil is removed. It can be used for creating lawns, beds and other garden work. Next, a pit is equipped. Weak soil removed from it (this can be peat, saline or marly clay soil, fine sand) is used for less critical work.
A rock cushion is placed at the bottom of the pit. Explosive soils of igneous origin (granite, basalt, diorite) are best suited for this purpose. Their unilateral compressive strength should be above 50 MPa.
When arranging a foundation in a wetland, you should pay attention to the softness and solubility of the components that make up the rocky soil. In particular, material with admixtures of gypsum, chalk, opoka, and saline rocks should be avoided. Otherwise, these components will be washed away over time, and the house will settle.
If you lay the foundation at frost depth, the rock bed will go through cycles of freezing and thawing several times a year. Over time, this will begin to affect the quality of the foundation underneath. For such important work, you should buy rock with frost resistance of at least F100-F150. When strengthening soil that does not freeze in winter, this indicator can be ignored. But on a solid rock it will still be high.
If you are going to build a house with 1-2 floors or an outbuilding, you can take collapsible soil of sedimentary origin (for example, limestone). Metamorphic soils (shales) have a layered structure. They are prone to lateral deformation, so they are not suitable for a foundation cushion on a slope.
As for the fraction, medium or large rocky soil is more suitable for this type of work. Even stones with dimensions of 700-800 mm can be placed in the base. They will create reliable support for the foundation.
Raising the level of the site
Rocky soil will be useful for site leveling work - for example, for leveling and raising the yard after construction is completed. You can fill the rock base with gravel, then lay paving slabs or pour concrete.
To raise the level of the site, you can buy almost any material. Here you can save money and take collapsible soil from sedimentary pores. It is worth choosing a small fraction. It compacts and levels out better.
Production of low grade concrete
Let's say right away that rocky soil is far from the best aggregate for concrete. However, if you have a small amount of this material left, and the task is not difficult, then you can use rock. For example, for concrete under fence posts or a small area in the yard, rocky soil is quite suitable.
For these purposes, you need to take a fine fraction. Large stones, over 120 mm, should be set aside. Over time, they can be used to decorate the garden (more on this a little later). If the material contains a lot of small clay particles, it must be sifted before use. But if the volume required is small, then it will be easier to select stones of suitable sizes from the general mixture.
When performing complex work, when a high-quality solution is needed, we recommend using crushed stone for concrete rather than rock.
Methods for improving loamy soil
To improve the fertility of loam, it is recommended to carry out preventive measures to change the structure and increase looseness. Every spring, it is recommended to dig up the soil, adding various types of leavening agents: sand, peat, rotted sawdust from deciduous trees, compost. You don’t have to wait for the sawdust to rot, but soak it in urea. You should not use reddish peat to loosen loamy soil; this will increase the iron content in the soil. In the fall, you can use manure; horse or sheep manure is best. Baking powder is applied to a depth of 10 to 15 cm, going deeper every year.
You can loosen the soil with compost
Loams are soils that are well moistened and dry out poorly. As a result, acidification occurs. Sawdust, manure or straw are used as deoxidizers. Dolomite flour is perfect - once every four years, no more than 500 grams per 1 square meter.
What is the predominant slope of the soil on such soil and what does it affect?
If it is realistic to level a site for the construction of a private house with other types of soil, then carrying out such work with natural rocky soils can be a very costly task. This point must be taken into account, because it is the topography of the site that will influence the style and design of the future building.
But if the site has rocky soil with a slope, then this has a plus, since here it will be possible to build a house with a basement without fear of landslides and other similar nuances.
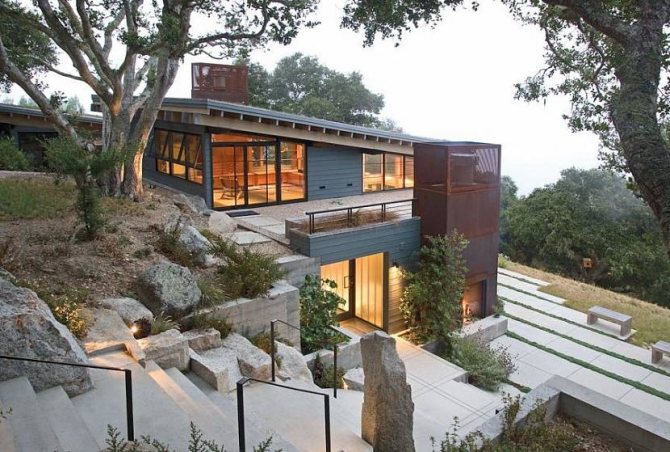

A house on a rocky site with a slope will cost more, but the result will justify yours Source yandex.ua
If the slope is small and amounts to 3-5%, then the preparatory work for laying the foundation additionally includes adding a cushion of sand and gravel. If there are significant differences - from 15%, this option will not work. In this case, it will be necessary to carry out more complex work, for example, the construction of multi-tiered houses, which are divided into separate horizontal platforms located on horizontal surfaces. In this case, it is best to use a stepped foundation.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in repairing foundations and building fences
Possible consequences
A thorough study of the soil and selection of the type of foundation will help you avoid mistakes during construction. The most common is tape, but its use on loamy soils should be done with caution. It is important to consider the level to which the ground can freeze. The foundation should be located several tens of centimeters lower. Otherwise, in a few years, after the change of seasons, cracks will appear in the concrete slabs. Such a house will be unsuitable and even dangerous for habitation. Often, repairing such a structure is impossible.
Types of soil
There are many types of soil. These include pure sand or clay, the processing of which, as a rule, causes many difficulties for gardeners. The sandy loamy rock also needs improvement: it is thoroughly fertilized before planting. But it is actively used in construction, especially in the construction of road surfaces.
Rocky soils are ideal for engineering work. However, they are quite rare. As for loam, it is a non-rocky type of soil. Due to its high clay content it is also called bound.

Also well suited for the construction of monumental structures and small buildings. However, the foundations of these buildings may be susceptible to failure due to increased moisture content. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately study the composition of the loam and determine the further procedure for construction.











